Surface area to volume ratio
The bigger a cell or structure is, the smaller its surface area to volume ratio is, slowing down the rate at which substances can move across its surface
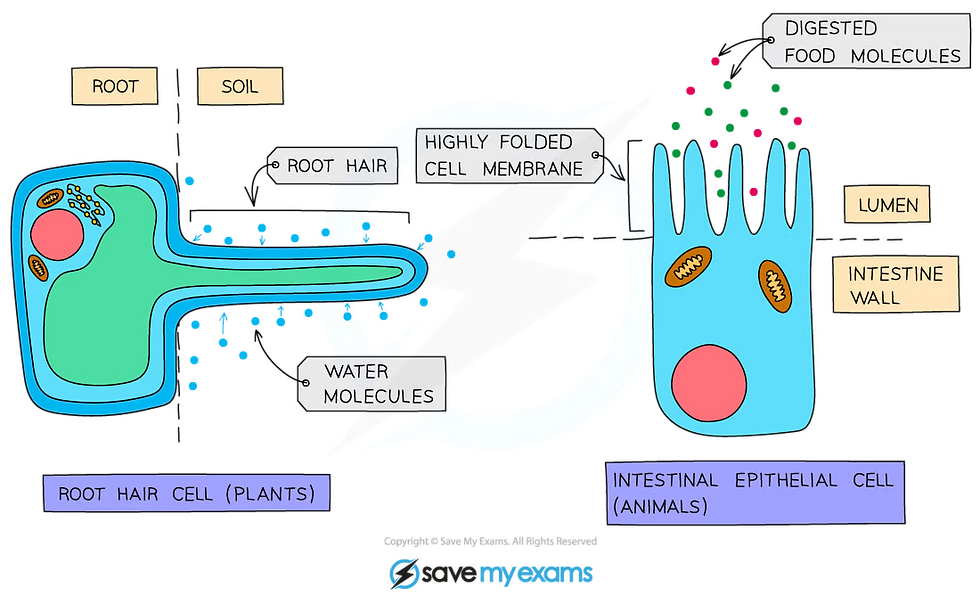
Many cells which are adapted for diffusion have increased surface area in some way - eg root hair cells in plants (which absorb water and mineral ions) and cells lining the ileum in animals (which absorb the products of digestion)
Cell adaptations for diffusion
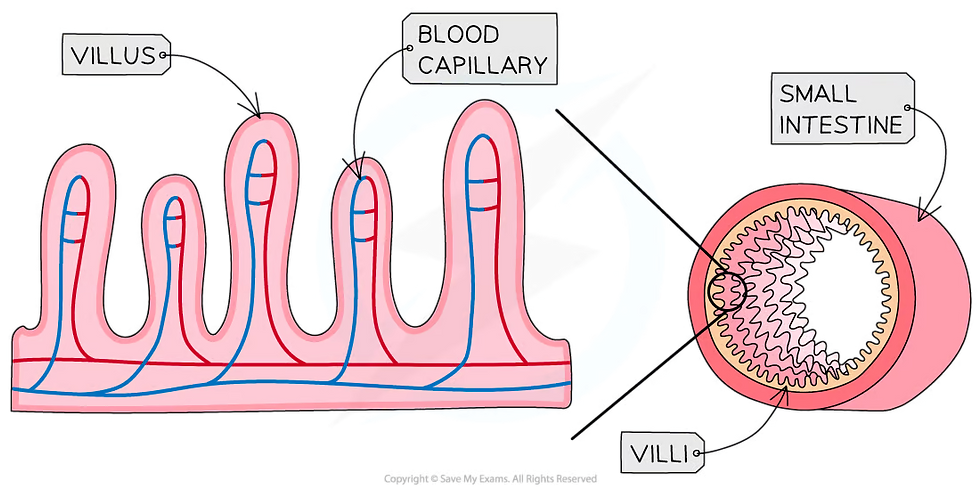
The highly folded surface of the small intestine increases its surface area
Distance
The smaller the distance molecules have to travel the faster transport will occur
This is why blood capillaries and alveoli have walls which are only one cell thick, ensure the rate of diffusion across them is as fast as possible
Temperature
The higher the temperature, the faster molecules move as they have more energy
This results in more collisions against the cell membrane and therefore a faster rate of movement across them
Concentration Gradient
The greater the difference in concentration on either side of the membrane, the faster movement across it will occur
This is because on the side with the higher concentration, more random collisions against the membrane will occur
Exam Tip
You should have carried out investigations into the factors that influence the rate of diffusion and as so should be able to use the information above to explain experimental results in an exam. You should also be able to plan and carry out an experiment which can investigate the effect of one of these factors.