Introduction
Many Reactions, such as muscle contraction, carbon fixation, etc, needs Energy.
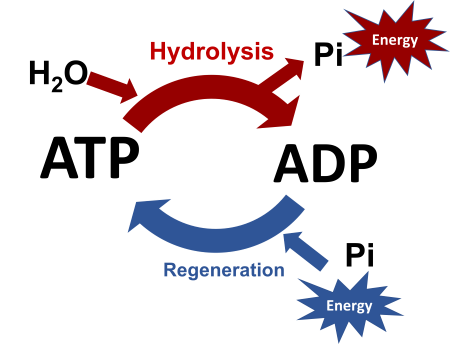
As ATP is the Energy Coin of our body, We break the Bond of ATP to create Energy.
ATP hydrolysis releases the energy present in the high-energy terminal phosphate bonds, which is utilised to carry out various cellular reactions.
ATP hydrolysis is an exergonic process. It produces ADP (Adenosine diphosphate), Pi (inorganic phosphate) and energy.
ADP can undergo further hydrolysis in some cases to produce AMP (Adenosine monophosphate) and Pi.
What's Happening
The ATP is getting added to the Water Molecule to create ADP and Pi and Energy.
ATP + H2O = ADP + Pi + Energy
When Added to Water :
Electrostatic repulsion: The four negative charges on the oxygens of the ATP molecule repel each other.
Solvation: HPO42-, H+, and ADP are more soluble than ATP, making it easier for ATP to lose a phosphate group.



What is mean by exergonic process?
Under what conditions or in what cellular contexts would ADP be hydrolyzed to AMP?
What is carbon fixation? it happen in animals?
How the energy released from ATP hydrolysis is utilized in carbon fixation?
What type of biomolecule is ATP?
Does hydrolysis of atp produces heat?
Does atp synthesis requires oxygen?
How do plants produce ATP?
What is the net ATP gain from one molecule?