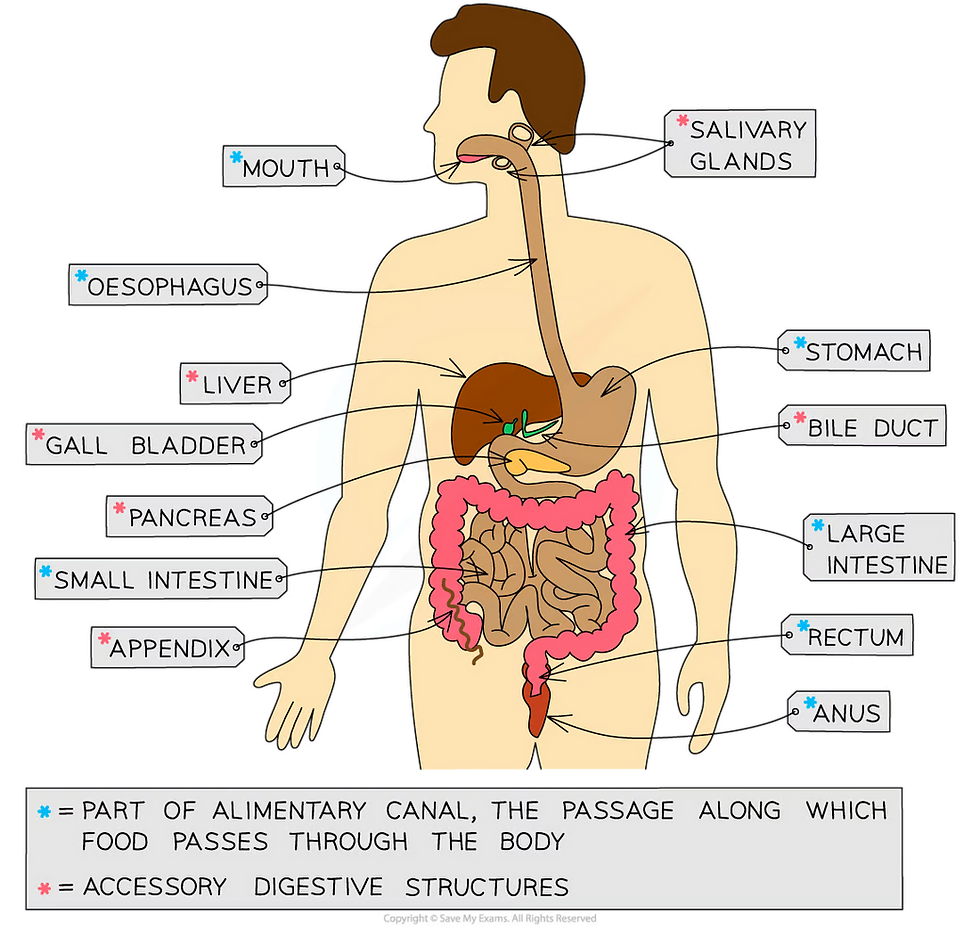
Digestive System : organs
The digestive system is an example of an organ system.
Some of the digestive system organs make up the alimentary canal; food passes directly through these organs as it moves through the body:
mouth
oesphagus
stomach
small intestine, including the duodenum and the ileum
large intestine, including the colon, rectum and anus
Some of the organs of the digestive system do not form part of the route travelled by food, but are still involved with digestion; these are the associated organs, or accessory organs, and include the:
salivary glands
pancreas
liver
gall bladder
Digestive system organs diagram
The organs of the human digestive system work together to digest food and absorb nutrients
Digestive system:function
The function of the digestive system is to digest food and absorb nutrients.
The digestive system carries out its function in several stages:
○ingestion: food and drink are taken into the body through the mouth
○ mechanical digestion: food is broken down into smaller pieces without chemical change to the food molecules.
○ chemical digestion: large, insoluble molecules are broken down into small, soluble molecules.
○ absorption: small food molecules and ions move through the wall of the intestine into the blood.
○ egestion: food that has not been digested or absorbed passes out of the body as faeces.
Once nutrients have been absorbed into the blood by the digestive system they can be assimilated into the body; this occurs when they are taken up by the cells of the body.





Where does most digestion take place?
What does the pancreas do for digestion?
What enzyme breaks down carbohydrates in the mouth?
What is the function of bile juice?
How does the body control the digestive process? Explain in detail.