To know what wifi is, we need to learn about waves.
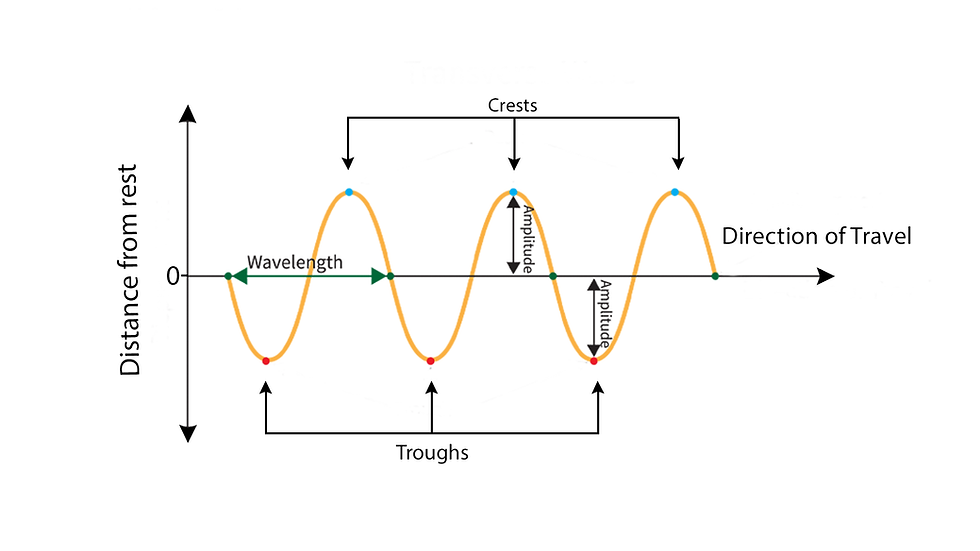
A wave is a disturbance in a medium that carries energy without a net movement of particles. Sound is an example of a wave.
There are two types of waves, Transverse and longitudinal.
Transverse wave-
A wave in which the medium vibrates at right angles to its propagation direction.
A ripple in water is an example; Light is also a transverse wave.
Longitudinal wave-
A wave vibrating in the direction of propagation.
Sound is a longitudinal wave. In a longitudinal wave, the Molecules, mostly air molecules, hit the molecules in front and create a compression and expansion state across the point from where it is created till the point it stops.

Reflection and refraction of waves-
Reflection-
Reflection is the bouncing back of light or sound when it hits a surface. When a light, for example, reflects, there are factors like Incident ray, reflected ray, angle of reflection, and angle of incident.

Refraction-
Refraction is the bending of a ray when it travels from one medium to another.

An optical fiber, or optical fiber, is a flexible glass or plastic fiber that can transmit light from one end to the other.











keywords
Phase change
Heat transfer
Fusion (melting)
Vaporization (boiling/evaporation)
Condensation
Sublimation
Freezing
Deposition
Energy absorption
Energy release
Specific latent heat
Thermodynamics
Cooling effect
Heat of fusion
Heat of vaporization