Covalent bonds in complex covalent molecules
Some atoms need to share more than one pair of electrons to gain a full outer shell of electrons
If two adjacent atoms share two pairs of electrons, two covalent bonds are formed, also known as a double bond
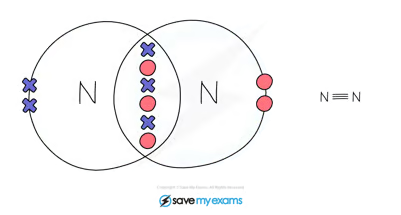
If two adjacent atoms share three pairs of electrons, three covalent bonds are formed, also known as a triple bond
Nitrogen:
When 2 nitrogen atoms react they share 3 pairs of electrons to form a triple bond
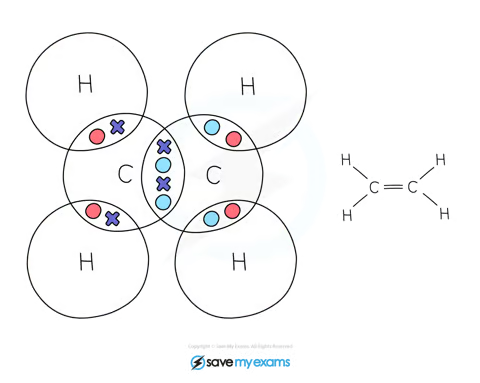
Ethene:
In ethene, the 2 carbon atoms share 2 pairs of electrons
This is known as a double bond
Properties of simple molecular compounds
Small molecules are compounds made up of molecules that contain just a few atoms covalently bonded together
They have low melting and boiling points so covalent compounds are usually liquids or gases at room temperature
As the molecules increase in size, the melting and boiling points generally increase
Small molecules have poor electrical conductivity
Explaining the properties of simple molecular compounds
Linking bonding and properties
Small molecules have covalent bonds joining the atoms together, but intermolecular forces that act between neighbouring molecules
They have low melting and boiling points as there are only weak intermolecular forces acting between the molecules
These forces are very weak when compared to the covalent bonds and so most small molecules are either gases or liquids at room temperature
As the molecules increase in size the intermolecular forces also increase as there are more electrons available
This causes the melting and boiling points to increase
Electrical Conductivity
Molecular compounds are poor conductors of electricity as there are no free ions or electrons to carry the charge.
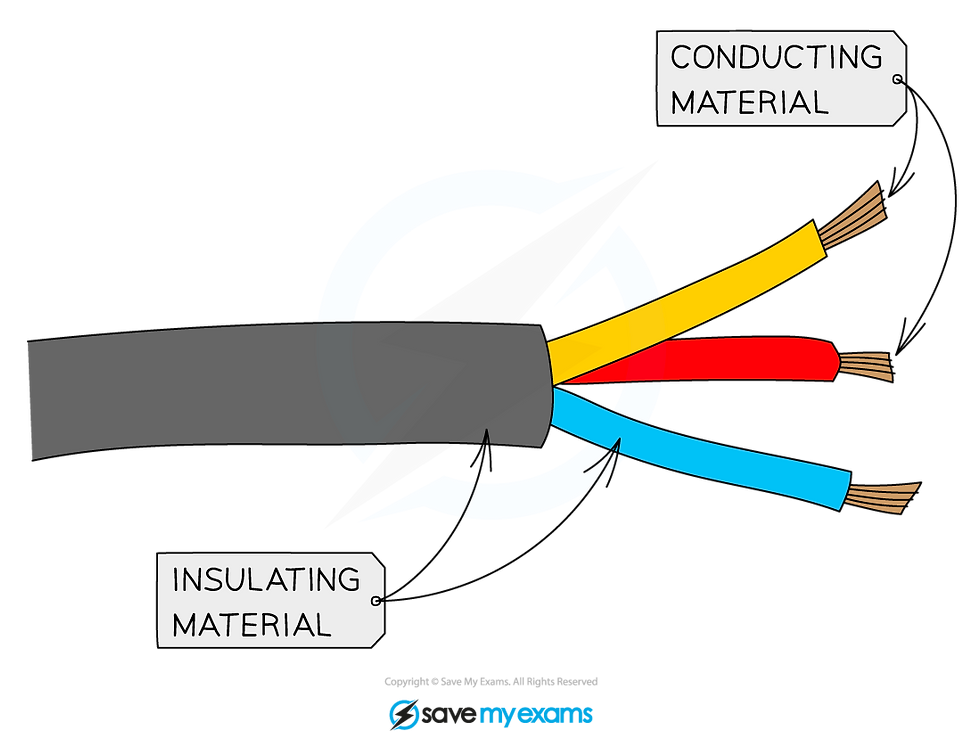
Most covalent compounds do not conduct at all in the solid state and are thus insulators
Common insulators include the plastic coating around household electrical wiring, rubber and wood