Relative masses
Relative atomic mass
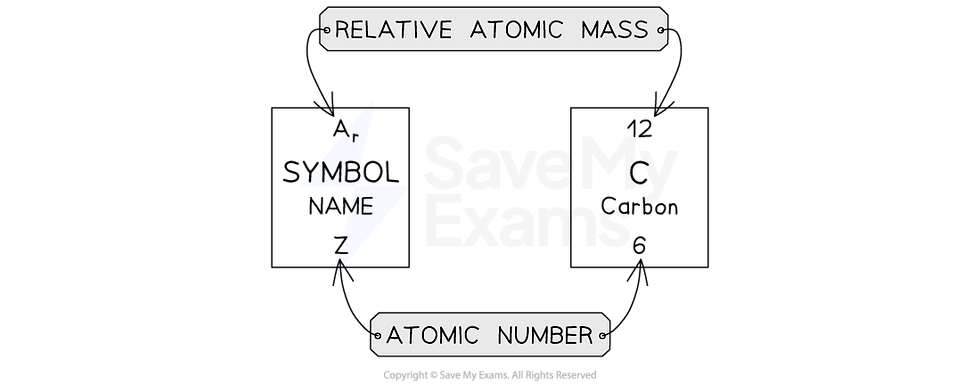
The symbol for relative atomic mass is Ar
The relative atomic mass for each element can be found in the Periodic Table, along with the atomic number
Relative atomic mass is shown on the atomic symbol
It is always larger than the atomic number (except for hydrogen, where they are the same)
Use the key on the Periodic Table to correctly identify the mass number
Atoms are too small to accurately weigh but scientists needed a way to compare the masses of atoms
Carbon-12 is used as the standard atom and has a fixed mass of 12 units
The mass of all other atoms are compared against carbon-12
The relative atomic mass of carbon is 12
The relative atomic mass of magnesium is 24 which means that magnesium is twice as heavy as carbon
The relative atomic mass of hydrogen is 1 which means it has one-twelfth the mass of one carbon-12 atom
Relative molecular (formula) mass
The symbol for the relative molecular mass is Mr
Relative molecular mass is the sum of the relative atomic masses of all the atoms in a molecule
The term relative formula mass is used when referring to the total mass of an ionic compound
To calculate the Mr of a substance, you have to add up the relative atomic masses of all the atoms present in the formula
Reacting masses
The Law of Conservation of mass tells us that mass cannot be created or destroyed
In a chemical reaction, the total mass of reactants equals the total mass of the products
We can use this, along with relative atomic / formula masses to perform calculations to identify the quantities of reactants or products involved in a chemical reaction
Example:
2Ca + O2 → 2CaO
Relative atomic masses: Ca = 40; O = 16
Using the balanced symbol equation:
Reactants:
2 x 40 = 80 units of mass of calcium
2 x 16 = 32 units of mass of oxygen (O2 molecule, 16 + 16 = 32)
Products:
2 x (40 + 16) = 112 units of mass of CaO
80 + 32 = 112
The ratio of the mass of calcium and oxygen reacting will always be the same, regardless of the units
80 g of calcium will react with 32 g of oxygen to form 112 g of calcium oxide
80 tonnes of calcium will react with 32 tonnes of oxygen to form 112 tonnes of calcium oxide
So, 40 kg of calcium will react with 16 kg of oxygen to form 56 kg of calcium oxide