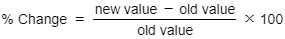The Definition & Calculation of PES
The law of supply states that when there is an increase in price (ceteris paribus), producers will increase the quantity supplied & vice versa
Economists are interested in how much the quantity supplied will increase
Price elasticity of supply (PES) reveals how responsive the change in quantity supplied is to a change in price
The responsiveness is different for different types of products
Calculating PES
PES can be calculated using the following formula
To calculate a % change, use the following formula
Worked Example For PES
In recent months, the price of avocados has increased from £0.90 to £1.45. Bewdley Farm Shop in Wales have sought to maximise their profits by increasing the quantity supplied to market. They have been able to increase the supply of avocados from 110 units a week to 120 units a week. Calculate the PES of avocados & explain one reason for the value
The PES value of 0.15 indicates that avocados are very price inelastic in supply. Even with a significant increase in price, suppliers are unable to supply more likely due to the time it takes to grow additional avocados